Boost Site Performance
A website’s loading speed is critically important, influencing both the visitor experience and its ranking in search engines. Research indicates that more than half of mobile users will abandon a site if it fails to load within three seconds. Since search engines like Google factor site speed into their ranking algorithms, slow sites are often penalized with lower visibility. By employing optimization techniques, a site with a six-second load time can often be accelerated to less than two seconds.
This guide details comprehensive strategies for maximizing site speed, covering fundamental necessities, simple steps, best practices, and advanced fine-tuning.

I. Core Principles of Site Speed
The Importance of Velocity With the average human attention span being very brief, you have minimal time to capture a visitor’s interest. A slow loading time risks users leaving before your content even appears. A study involving major online platforms found that a single one-second delay in loading time can cause a 7% drop in conversions, an 11% reduction in page views, and a 16% decrease in customer satisfaction. To increase traffic, subscribers, and revenue, your website must be fast.
Checking Your Website’s Speed Accurately Site owners often mistakenly believe their website is fast because it loads quickly on their own computers. This occurs because modern browsers cache (save) the site’s data locally, making subsequent visits appear instantaneous. However, a new visitor in a different geographic location will experience the true load time. The optimal goal for any website is a load time under two seconds.
Key Causes of Sluggish Performance Multiple factors commonly contribute to slow loading times:
- Web Hosting: If the server is improperly configured or resources are overstretched, performance suffers.
- Configuration: A lack of caching forces the server to dynamically generate pages for every visitor, which overloads the server.
- Page Size: Unoptimized images and excessive file sizes significantly increase download time.
- Defective Plugins: Poorly coded extensions can consume excessive resources, slowing down the entire operation.
- External Scripts: Third-party elements, such as ads or font loaders, can introduce delays.
The Necessity of High-Quality Hosting The hosting service is foundational to performance. While good shared hosting providers make efforts to optimize speed, you are sharing resources with many other accounts. Managed hosting services, like SiteGround, offer server configurations precisely optimized for websites, often including additional benefits like automated backups and enhanced security.
II. Easy Performance Steps (No Coding)
For those uncomfortable with making manual changes, services are available. For example, WPWatch Pro Services offers an affordable site speed optimization service that handles caching setup, CDN configuration, image compression, and lazy loading for you.
If you choose to do it yourself, you can achieve significant gains with minimal effort:
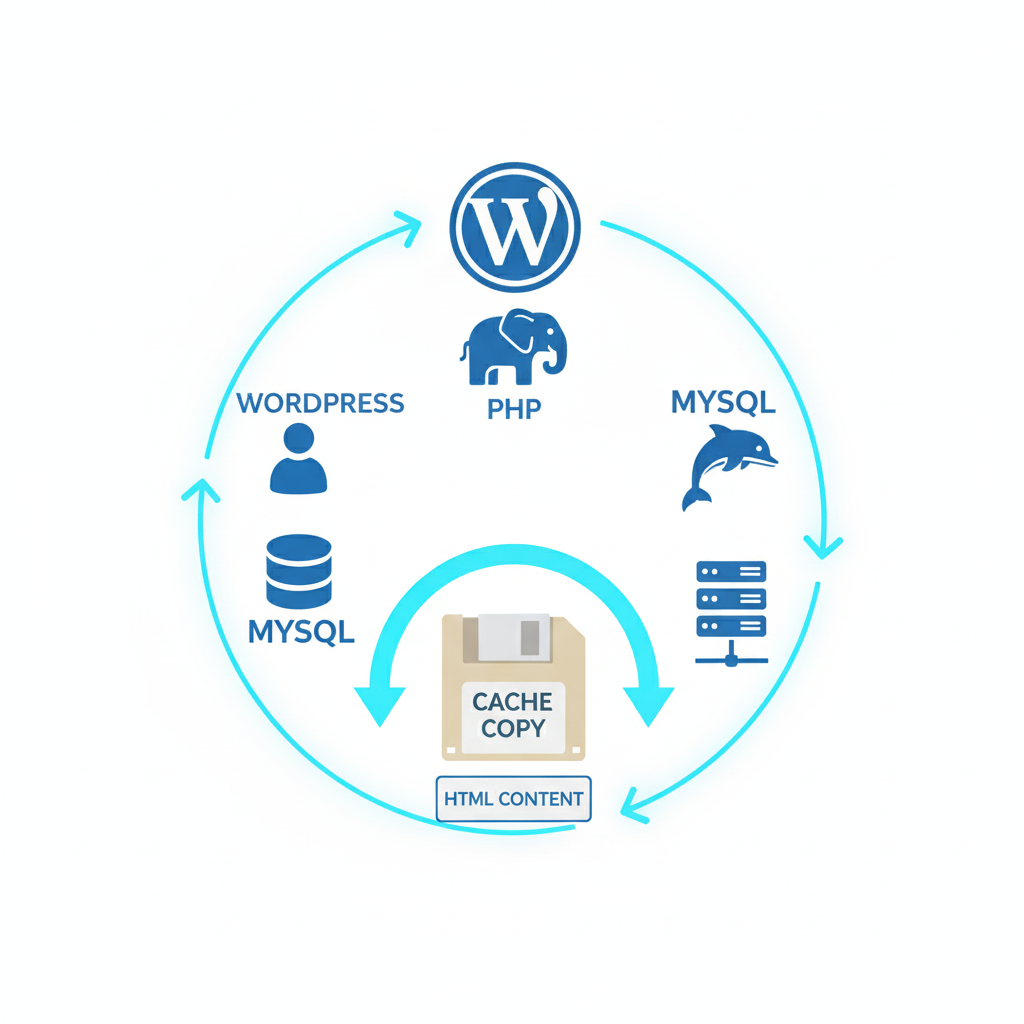
1. Implement a Caching Plugin Because website pages are generated dynamically upon every visit (requiring data retrieval and assembly), this is a slow process under high traffic. A caching plugin resolves this by creating and serving a static HTML copy of the page after its initial load. This can make your site two to five times faster. Highly recommended options are WP Rocket (premium) or WP Super Cache (free).
2. Optimize Images Unoptimized images are a leading cause of slow load times. Ensure you compress images to reduce file size without losing quality and choose the right format (e.g., JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics).
III. Best Practices for Lasting Speed
- Keep Software Current: Regularly update your platform, themes, and plugins to leverage the latest performance and security enhancements.
- Streamline Background Processes: Optimize or limit non-visible, scheduled tasks like automatic backups.
- Use Summaries on Archive Pages: Display post excerpts instead of the full content on your homepage and category pages to keep initial page weights low.
- Split Comments: For popular posts, paginate comments across multiple pages to prevent long comment threads from hindering load times.
- Deploy a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN duplicates your site’s static assets (images, stylesheets) across global servers, delivering them from the nearest location to each user for superior worldwide speed.
- Embed Media, Don’t Upload: Avoid uploading audio and video directly to your server; use third-party services (like YouTube or Vimeo) and embed the content.
- Select Optimized Themes and Plugins: Choose lightweight themes built for speed and use only well-coded plugins from reputable developers.
IV. Advanced Tuning for Maximum Results
These techniques are more technical and may involve modifying core files; ensure you have a full backup before proceeding.
- Paginate Long Content: While comprehensive articles are great for SEO, those with excessive images can slow down. Use the built-in pagination feature to split lengthy posts into multi-page series.
- Reduce External HTTP Requests: Many themes and plugins fetch resources (scripts, stylesheets) from outside sources. Too many of these external calls can introduce lag. You can mitigate this by merging or disabling non-essential third-party scripts.
- Minimize Database Queries: Poorly written themes often make unnecessary database requests. Selecting well-coded themes and optimizing your database can resolve this issue.
- Limit Post Revisions: Control the number of revisions stored in the database to prevent unnecessary bloat.
- Block Content Leeching: Prevent other websites from directly linking to and using your site’s images (hotlinking), which consumes your bandwidth.
- Implement Lazy Loading: Configure images and media to load only when they enter the user’s viewport, dramatically improving the page’s initial paint time.
- Use a DNS-Level Firewall: Implement a high-performance security firewall to boost both speed and defense.
- Correct SSL Errors: Fix any Secure Sockets Layer/HTTPS configuration issues without relying on a dedicated plugin.
- Utilize the Latest PHP Version: Running the most recent stable version of PHP is crucial, as newer versions often provide substantial performance gains.
